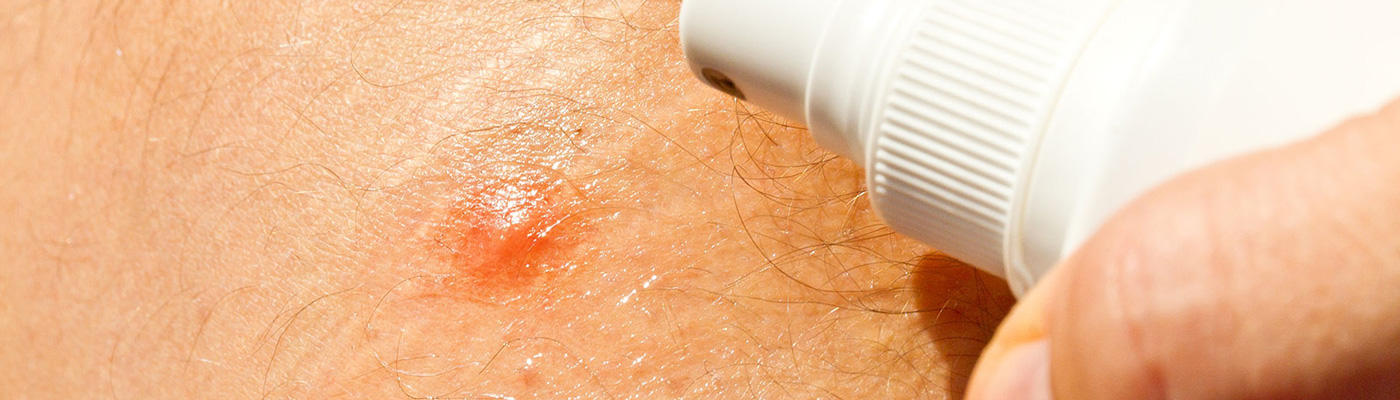
Insect stings and bites are an expected summertime nuisance, causing temporary discomfort and pain, but no serious or lasting health problems. However, they can cause infections that require treatment and allergic reactions that can be serious, even fatal.
Symptoms
Symptoms of local skin reactions at the sting site or surrounding area include swelling, redness, itching, warmth, hives, and small amounts of bleeding or drainage. Generalized symptoms that indicate a more serious and life-threatening allergic reaction include coughing, tickling in the throat, tightness in the throat or chest, breathing problems or wheezing, nausea or vomiting, dizziness or fainting, sweating, anxiety, itching, and a rash elsewhere on the body, remote from the sting site.
Specific treatment for stings will be determined by your healthcare provider. Large local reactions usually do not lead to generalized reactions. However, they can be life-threatening if the sting occurs in the mouth, nose, or throat from swelling that can close off the airway.
Treatment
In the event of an insect sting, try to remain calm. If possible, remove the stinger by gently scraping across the site with a blunt-edged object, such as a credit card or dull knife. Do not try to pull it out, as this may release more venom. Wash the area thoroughly with soap and water and apply a cold pack wrapped in a cloth to reduce swelling and pain (10 minutes on and 10 minutes off for 30 to 60 minutes). If the sting occurs on an arm or leg, elevate the limb to help reduce swelling.
To reduce itching, apply a paste (baking soda, non-seasoned meat tenderizer or a wet tea bag and water) and leave it on for 15 to 20 minutes. There are also several over-the-counter products available to use on insect stings, such as an antihistamine, corticosteroid cream, or calamine lotion. You may want to take acetaminophen for pain or an over-the-counter antihistamine, if approved by your healthcare provider.
Call 911 or your local emergency medical service and seek emergency care immediately if you or a loved one are stung in the mouth, nose, or throat area or have any signs of a generalized reaction. Emergency medical treatment may include intravenous antihistamines, epinephrine, corticosteroids or other medications, lab tests and breathing support.
Prevention
General guidelines to reduce the possibility of insect stings and prevent an allergic reaction include avoiding perfumes, hairsprays, scented products, brightly colored clothing near locations of hives and nests. Spray your clothing with insect repellent and if an insect comes near, try to stay calm and walk away slowly.
If you know that you are prone to allergic reactions, consider carrying a bee sting kit (such as EpiPen) at all times and make sure you know how to use it. These products are available by prescription. Also, you may want to wear long-sleeve shirts and long pants when outdoors.
For more information, see an allergist for allergy testing and treatment.